Connection Oriented and Connectionless Services
In this tutorial, we will be covering the difference between two ways of establishing a connection that is Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Services in Computer Networks.
In order to establish a connection between two or more devices, there are services in Computer Networks. There are two services that are given by the layers to layers above them. These services are as follows:
-
Connection-Oriented Service
-
Connectionless Services
Connection-Oriented Services
There is a sequence of operations to be followed by the users of connection-oriented service. These are:
-
The connection is established.
-
Information is sent.
-
The connection is released.
In connection-oriented service, we have to establish a connection before starting the communication. When the connection is established, we send the message or the information and then we release the connection.
Connection-oriented service is more reliable than connectionless service. We can send the message in a connection-oriented service if there is an error at the receiver's end. An example of connection-oriented is TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) protocol.
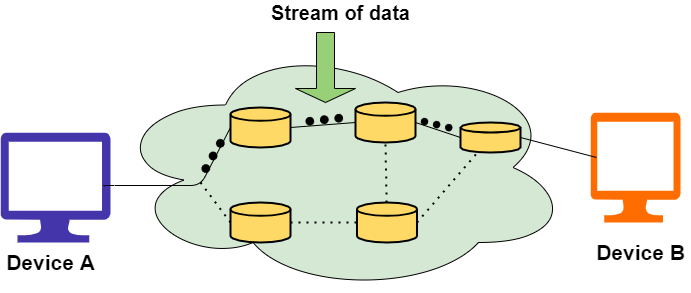
In the above diagram, a solid line between Device A and Device B indicates that there is a dedicated link with which the stream of data travels between them. With the help of this link, a receiver can send an acknowledgment to the sender about the status of the packet.
Advantages
Benefits of Connection-Oriented Services are as follows:
-
Connection-Oriented Services are reliable.
-
There is no duplication of data packets.
-
There are no chances of Congestion.
-
These are Suitable for long connections.
-
Sequencing of data packets is guaranteed.
Disadvantages
Drawbacks of Connection-Oriented Service are as follows:
-
This allocation of resources is mandatory before communication.
-
The speed of connection is slower. As much time is taken for establishing and relinquishing the connection.
-
In the case of Network Congestion or router failures, there are no alternative ways to continue with communication.
Connection Less Services
It is similar to the postal services, as it carries the full address where the message (letter) is to be carried. Each message is routed independently from source to destination. The order of messages sent can be different from the order received.
In connectionless the data is transferred in one direction from source to destination without checking the destination is still there or not or if it prepared to accept the message. Authentication is not needed in this. An example of a Connectionless service is UDP (User Datagram Protocol) protocol.

Advantages
Benefits of Connection Less Services are as follows:
-
There are usually low overheads.
-
Connection-Oriented services help to broadcast or multicast messages to multiple recipients.
-
In this, there is no circuit setup. Thus it takes a fraction of a minute in order to establish a connection.
-
In the case of Network congestion or router failures, it has an alternative path of data transmission.
Disadvantages
Drawbacks of Connection fewer services are as follows:
-
These are susceptible to congestion in the network.
-
It is not reliable as there is the possibility of a loss of data packets, wrong delivery of packets or duplication is high.
-
In this, each data packet needs lengthy fields because these are supposed to hold all the destination addresses and the routing information.
Let us understand the differences between the above given two services:
| Connection-Oriented Services |
Connection Less Services |
| Connection-Oriented services are designed on the basis of the Telephone System. |
Connectionless services are based on the Postal System. |
| In this type of service, a prior connection needs to be established. |
In this type of service, no prior connection is needed. |
| These services Ensure the reliable transfer of data. |
As these services are best efforts services but reliability is not guaranteed in these. |
| There is no possibility of congestion. |
There are chances of occurrence of congestion using these services. |
| In this authentication is required before transmitting the data packets to the receiver. |
In this, authentication is not required before transmitting the data packets to the receiver. |
| These services are suitable for long and steady transmissions. |
These services are suitable for bursty transmissions. |
| In this connection is established through the process of signaling |
There is no such signaling concept exists. |
| In this type of service, data packets travel towards their destination node in a sequential manner. |
In this type of service, data packets travel towards their destination node in a random manner. |
| Retransmission of lost data bits is possible. |
In this, it is not possible. |
| Delay is more while transferring the information. But after the establishment of connection, these services offer fast delivery of information. |
Due to the absence of the connection establishment phase, there is no delay. |
What are Service Primitives?
A service is formally specified by a set of primitives (operations) available to a user process to access the service. These primitives tell the service to perform some action or report on an action taken by a peer entity. If the protocol stack is located in the operating system, as it often is, the primitives are normally system calls. These calls cause a trap to kernel mode, which then turns control of the machine over to the operating system to send the necessary packets. The set of primitives available depends on the nature of the service being provided. The primitives for connection-oriented service are different from those of connection-less service. There are five types of service primitives :
-
LISTEN: When a server is ready to accept an incoming connection it executes the LISTEN primitive. It blocks waiting for an incoming connection.
-
CONNECT: It connects the server by establishing a connection. The response is awaited.
-
RECIEVE: Then the RECIEVE call blocks the server.
-
SEND: Then the client executes SEND primitive to transmit its request followed by the execution of RECIEVE to get the reply. Send the message.
-
DISCONNECT: This primitive is used for terminating the connection. After this primitive one can't send any message. When the client sends the DISCONNECT packet then the server also sends the DISCONNECT packet to acknowledge the client. When the server package is received by client then the process is terminated.
Connection-Oriented Service Primitives
There are 5 types of primitives for Connection-Oriented Service :
| LISTEN |
Block waiting for an incoming connection |
| CONNECTION |
Establish a connection with a waiting peer |
| RECEIVE |
Block waiting for an incoming message |
| SEND |
Sending a message to the peer |
| DISCONNECT |
Terminate a connection |
Connectionless Service Primitives
There are 4 types of primitives for Connectionless Oriented Service:
| UNIDATA |
This primitive sends a packet of data |
| FACILITY, REPORT |
Primitive for enquiring about the performance of the network, like delivery statistics. |
Relationship of Services to Protocol
In this section, we will learn about how services and protocols are related and why they are so important to each other.
What are Services?
These are the operations that a layer can provide to the layer above it in the OSI Reference model. It defines the operation and states a layer is ready to perform but it does not specify anything about the implementation of these operations.

What are the Protocols?
These are a set of rules that govern the format and meaning of frames, messages or packets that are exchanged between the server and client.