El Niño is characterized by unusually warm ocean temperatures in the Equatorial Pacific Ocean. El Niño is an oscillation of the ocean-atmosphere system in the tropical Pacific having important consequences on weather around the globe.
THE ORIGIN OF THE NAME EL NIÑO
El Niño was originally recognized by fisherman off the coast of South America as the appearance of unusually warm water in the Pacific Ocean, occurring near the beginning of the year. Every three to seven years during the months of December and January, fish in the coastal waters off of these countries virtually vanish, causing the fishing business to come to a standstill. El Niño means The Little Boy or Christ Child in Spanish. This name was used for the tendency of the phenomenon to arrive around Christmas.
As of now Scientists do not have any exact reason for its occurence.
CAUSES
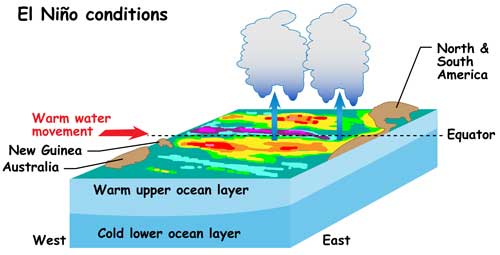
El Niño is caused by the warming of the Pacific Ocean and weakening of the Trade winds from South America to Asia. It occurs every four to five years.
IMPACT ON BIOSPHERE
- Phytoplanktons living near the surface depends upon nutrients for survival. In turn, fish and mammals depend upon phytoplankton as the very foundation of the marine food chain. The warm surface waters of an El Niño prevent the nutrients to accumulate as massive water evaporation takes place duw to warm water, effectively starving the phytoplankton population there and those animals higher up the food chain that depend upon it. Fishermen in Peru and Ecuador generally suffer heavy losses in their anchovy and sardine industries.
- It leads to increased rainfall across the southern tier of the US and in Peru, which has caused destructive flooding, and drought in the West Pacific, sometimes associated with devastating brush fires in Australia.
- It can play havoc on the farmers and global agricultural market especially to countries like Thailand, Vietnam and India who are world’s largest producers of rice.
- Extreme weather conditions related to the El Niño cycle correlate with changes in the incidence of epidemic diseases. For example, the El Niño cycle is associated with increased risks of some of the diseases transmitted by mosquitoes, such as Malaria, Dengue, and Rift Valley fever. Cycles of malaria in India, Venezuela, Brazil, and Colombia have now been linked to El Niño.