A Linked List is a data structure, where data nodes are linked together forming a chain or list.
A Linked list is made up of nodes, where a node is made up of two parts:
-
Data Part: Holds the data
-
Address Part: Holds the address of the next node.
Below we have a simple pictorial representation of Nodes connected to form a Linked List.
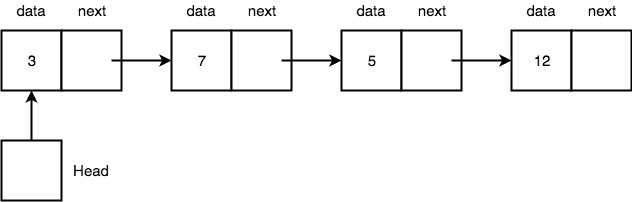
As you can see, every node has some data stored in it, and it also stores the location of the next node. It is not necessary that all the nodes get saved in contiguous memory locations, next to each other, that is why we need to store the location of the next node in the previous node to be able to access it like its a chain or list.
Head is a pointer that always points to the first node of the list if Head points to nothing, it means the linked list is empty.
Implementing Linked List
To implement a Linked List, we will first define a class for Node which will have two attributes, namely data and next, where next is the pointer to store the location of the next node.
Then we will have the class LinkedList, which will have the head pointer, initialized to None. We can also have another attribute size to store the size of the linked list.
Inserting Nodes
In this implementation of the Linked List, we will always insert data from the beginning, where we have the head pointer. In other words, the head pointer will always point to the first node of the linked list.
If you want to implement a linked list, in which you can insert a new node even from the end, then you can have another pointer tail which will point to the last node of the linked list.
Inserting a new node into the linked list has constant time complexity because it will always be added to the head pointer.
Find a Node
To find a node in the linked list, we have to traverse the list, comparing the value that we are looking for against data stored in every node.
Following will be steps followed:
-
Start from head pointer
-
Compare data stored in each node with the value given,
-
Repeat the above steps, until we find the value we are looking for or we reach the end of our linked list.
Deleting Data from Linked List
As already discussed above, we now know how to find a node in the linked list. In the case of deleting the node, all we have to do is find the node in the linked list and then remove it. To remove it we follow the following steps:
-
We need to have two pointer curr(current) and prev(previous). We need a pointer to the previous node because once the current node is removed, the previous node will have to store the address of the node pointed by the current node.
-
curr: Initially points to head
prev: Initially points to None
-
We will be traversing the linked list, starting from the head
-
If the value to be deleted, matches the data pointed by curr pointer, check if prev holds a value,
-
If Yes, then set next attribute of the pred node to the next node of the curr node. This will remove the node pointed by the curr pointer from the linked list.
-
If No, it means we want to remove the first node of the linked list. Simply make the head point to the next node of the curr node.
-
Decrement the size count by 1.
-
Return True.
-
If the value to be deleted, doesn't match the data pointed by the curr node, then move ahead, by pointing prev pointer to current node and curr pointer to the next node.
-
This is repeated until we reach the end of the linked list. If we are unable to find the value to be deleted, then return False.
NOTE: In the code above we haven't added the code for allowing the user to insert a new node directly to the end of the linked list, you should try to add that to the LinkedList class.
Advantages of a Linked List
-
Insertion and Deletion are very easy, in case of Linked List, because all we have to do is an update next pointer.
-
We can easily implement Stack and Queue data structures using Linked List.
Disadvantages of a Linked List
-
Random access is not possible, to access any node we must traverse the Linked List. That is why it is said if you want to carry out insertion and updation on a set of data using Linked List, but if you want to traverse and search for data, an array is better.
You may also like: